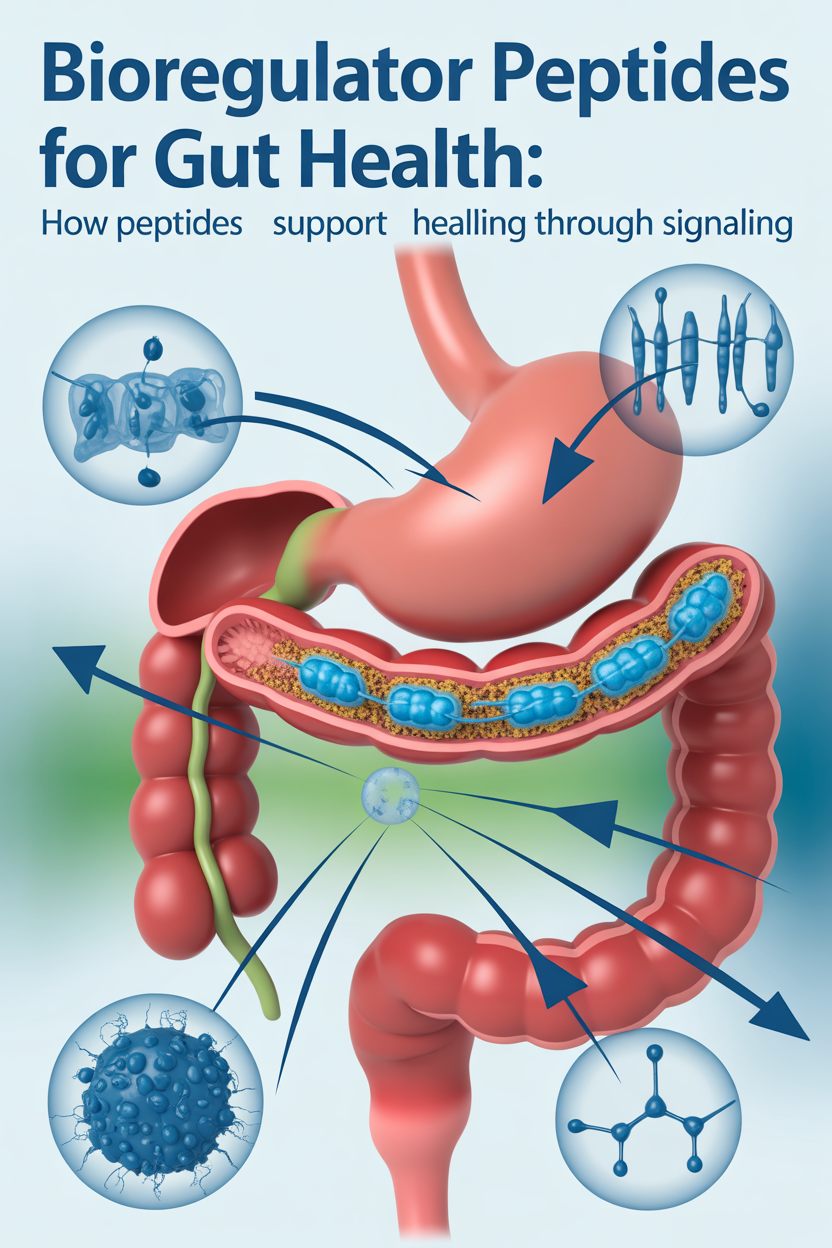
Bioregulator Peptides for Gut Health: How Peptides Support Healing Through Signaling
Bioregulator peptides for gut health, peptides for gut health, BPC-157 for gut health, peptide signaling, gut inflammation, mucosal barrier, immune regulation, nervous system signaling, gut healing, digestive health.
Gut health is regulated, not forced. Digestion, immune tolerance, barrier integrity, and motility depend on coordinated signaling between the gut, nervous system, immune system, and drainage pathways. When this signaling is disrupted, symptoms can persist even with dietary changes, supplements, or microbial interventions.
Peptides and bioregulator peptides are increasingly discussed in gut health conversations because they are studied as signaling molecules, not nutrients or drugs. Their relevance to gut health depends on how they interact with regulation, not on their ability to override physiology.
FAQ
What do peptides do for your gut?
Peptides function as signaling molecules that influence communication related to tissue repair, immune response, and barrier behavior.
Are bioregulator peptides supplements?
No. Bioregulator peptides are discussed in research as short-chain regulatory signals, often described as tissue-specific, rather than nutritional inputs.
Can BPC-157 heal the gut?
No single peptide heals the gut independently. Research discussions focus on signaling and repair models, not guaranteed outcomes.
What is the best peptide for gut health?
There is no universal answer. Gut response depends on system regulation, not on a single compound.
Gut health is regulated by signaling, not digestion alone
The gut functions as a coordination center. Immune behavior, inflammatory tone, and tolerance are shaped by signaling between systems rather than by digestion alone. This relationship is explored in How Gut Health Shapes the Immune System, which explains how gut signaling influences immune activation and suppression.
When signaling is impaired, the gut may remain reactive despite dietary modification or supplementation.
What peptides and bioregulator peptides are
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that act as biological messengers. Bioregulator peptides are discussed in research literature as signaling compounds associated with specific tissues.
Their relevance to gut health lies in how they interact with regulatory pathways rather than in direct antimicrobial or nutritional effects. This distinction aligns with the framework outlined in Terrain vs. Bugs: Why Killing Isn’t the First Step, where regulation precedes intervention.
Immune signaling and mucosal barrier integrity
Barrier integrity influences immune behavior. When signaling at the mucosal layer is disrupted, immune responses may become exaggerated or inappropriate. This relationship is detailed in Healing the Mucosal Barrier: The Forgotten Layer of Gut Health, which focuses on how barrier signaling shapes immune tolerance.
Peptides discussed in gut research often relate to signaling pathways involved in tissue response and immune modulation rather than direct structural repair.
Nervous system regulation and gut response
Gut motility, secretion, and sensitivity are influenced by nervous system input. Dysregulation in autonomic signaling can impair digestion and contribute to symptoms such as bloating or irregular motility.
This connection is explored in Gut Health Starts in the Nervous System: The Real Cause of Bloating and IBS, which outlines how nervous system state affects gut signaling and responsiveness.
Why terrain determines whether signaling works
Signaling depends on clearance. When bile flow, lymph movement, or bowel elimination are impaired, inflammatory byproducts recirculate and interfere with immune and repair signaling. This relationship between gut function and systemic clearance is outlined in The Gut–Liver–Lymph Axis Explained: Why This Detox Trio Controls Your Drainage, where gut signaling is shown to be inseparable from downstream detox pathways.
For deeper education on regulatory signaling, immune coordination, and gut system stability, Health Foundations provides expanded context.
The article continues below for Health Foundations members, with deeper education on how regulatory signaling affects gut stability and repair.